见下一个文章
【NFS】Ubuntu安装nfs服务器及使用教程 – 天英科技创新协会
1、nfs指令是否支持
可以通过编译uboot源码,menuconfig勾选来实现,具体编译方法不在此描述。
2、nfs指令使用
nfs 80800000 192.168.1.200:/home/xiaobao/workspace/nfs/rootfs/Imagenfs指令通过挂在192.168.1.200远端NFS服务器,把镜像文件Image加载到内存80800000
3、NFS版本兼容
解决方案:
【NFS】VFS: Unable to mount root fs via NFS. [ 115.256801] devtmpfs: mounted【NFS】 – 天英科技创新协会
4、加载超时一直打印TTTTTTTTTTTTTTT
解决方案:
编辑服务端 /etc/hosts 文件:
sudo vim /etc/hosts添加开发板 IP 和服务端 NFS 共享文件目录:
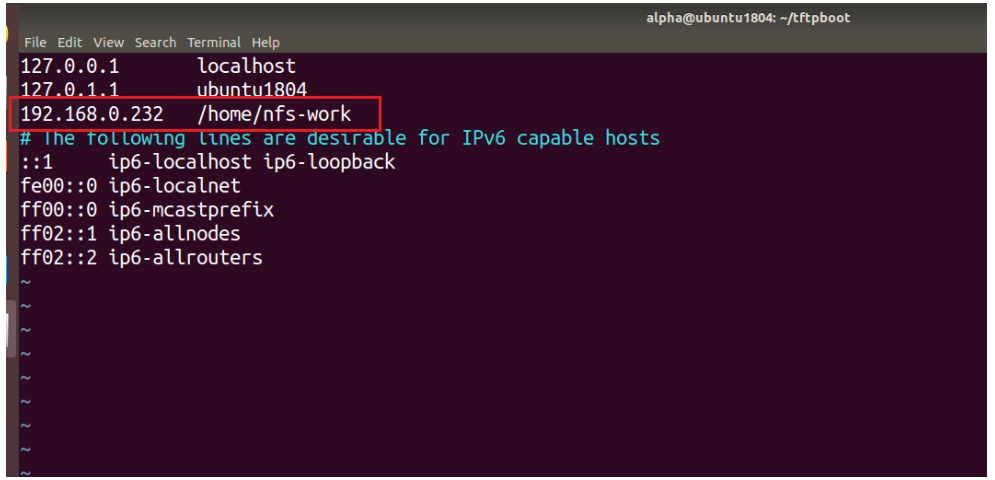
再次重启 NFS 服务:
sudo service nfs-kernel-server restart1、支持nfs客户端及网络环境
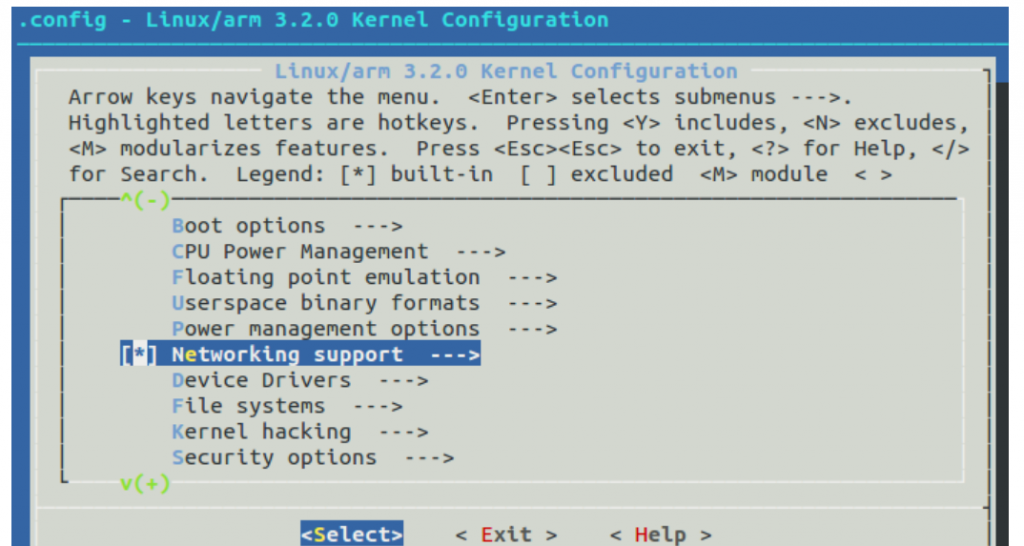
配置网络部分
Networking support
Networking options
TCP/IP networking
IP: kernel level autoconfiguration
[*] IP: DHCP support
[*] IP: BOOTP support
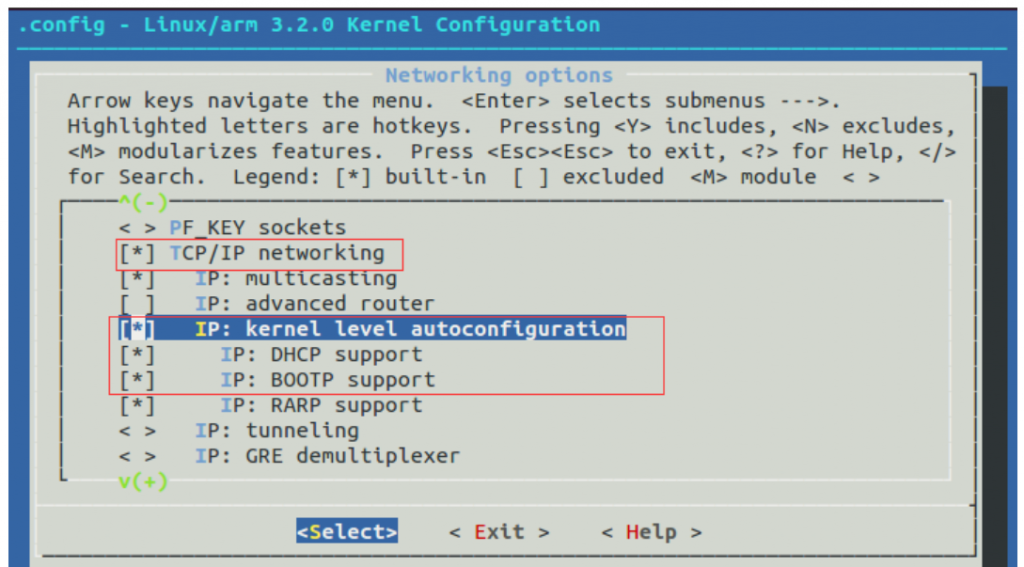
配置开启nfs服务
File systems
Network File Systems
<*> NFS client support
[*] NFS client support for NFS version 3
[*] NFS client support for the NFSv3 ACL protocol extension
[*] NFS client support for NFS version 4
[*] Root file system on NFS
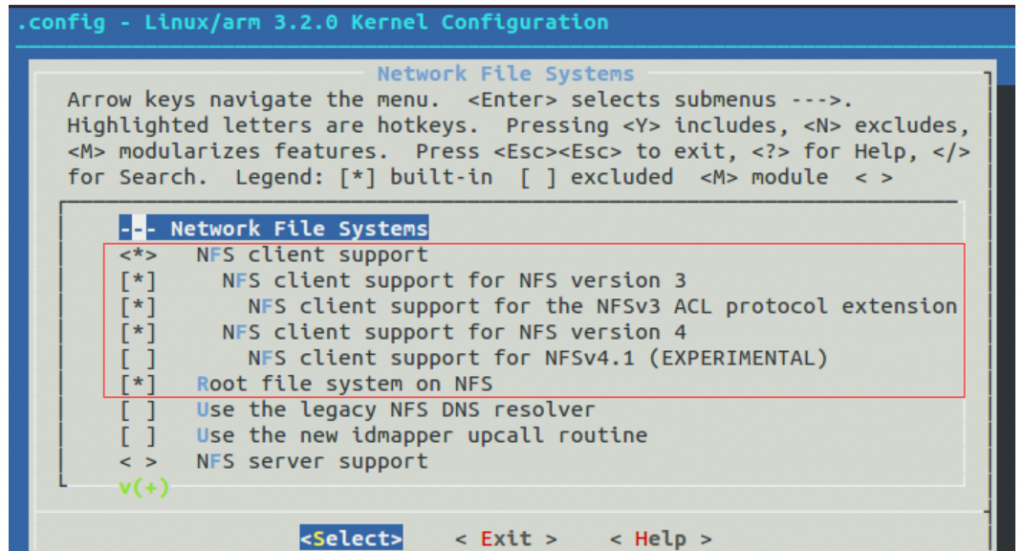
uboot启动参数配置
setenv bootargs root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=172.16.27.200:/home/xiaobao/workspace/nfs/rootfs ip=dhcp console=ttyAMA1,115200 earlycon=pl011,0x20001000 rootdelay=10 rw启动直接挂载远端NFS
国产飞腾芯片s5000c-16
国产网讯网卡WX1860AL2
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu Built with Buildroot, based on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Release: 22.04
Codename: jammy
直接从官网下载就好,本实现使用的版本:ngbe-1.2.7.zip
不同平台上编译,安装的命令不同:
•Kylin V10/银河麒麟 操作系统:
编译:
make CHNOS=KYLIN
安装:
make CHNOS=KYLIN modules_install
或者
make CHNOS=KYLIN install
•UOS 操作系统:
编译:
make CHNOS=UOS
安装
make CHNOS=UOS modules_install
或者
make CHNOS=UOS install
•Euler 操作系统:
编译:
make CHNOS=EULER
安装:
make CHNOS=EULER modules_install
或者
make CHNOS=EULER install
•其他平台操作系统:
编译:
make
安装:make modules_install
或者
make install
4) 加载驱动:
modprobe txgbe (仅安装完首次需要手动加载,若重启系统,系统会自动加载驱动)。
5)查看驱动是否加载成功:
[root@SW ~]# lsmod | grep txgbe
txgbe 208399 0
表明驱动已经加载上。
1)显示已安装的驱动:
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod | grep txgbe
txgbe 385024 0
2)卸载驱动:rmmod txgbe
[root@localhost ~]# rmmod txgbe
3) 再次查看已安装的驱动,已经没有 txgbe 驱动。
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod | grep txgbe
1, 首先,为什么会出现修改了kernel重新编译后magic num改变
内核版本是如何生成的:
Linux 内核在进行模块装载时先完成模块的 CRC 值校验,再核对 vermagic 中的字符信息,linux版本在 include/generated/utsrelease.h中定义,文件中的内容如下:
#define UTS_RELEASE "4.9.123"
utsrelease.h是kernel编译后自动生成的,用户更改里面的内容不会有效果。
这个值可以通过修改最顶层的Makefile文件来修改。
VERSION = 4
PATCHLEVEL = 9
SUBLEVEL = 123
EXTRAVERSION =
...
在init/version.c中,定义了kernel启动时的第一条打印信息:
/* FIXED STRINGS! Don't touch! */
const char linux_banner[] =
"Linux version " UTS_RELEASE " (" LINUX_COMPILE_BY "@"
LINUX_COMPILE_HOST ") (" LINUX_COMPILER ") " UTS_VERSION "\n";
const char linux_proc_banner[] =
"%s version %s"
" (" LINUX_COMPILE_BY "@" LINUX_COMPILE_HOST ")"
" (" LINUX_COMPILER ") %s\n";
这里UTS_RELEASE在kernel编译时自动生成
在init/main.c的asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)函数中,有kernel启动的第一条打印信息,这条信息是dmesg命令打印出来:
pr_notice("%s", linux_banner);
驱动模块的version magic信息是怎么生成的:
4.x 内核下,在include/linux/vermagic.h中定义有VERMAGIC_STRING,如下:
#include <generated/utsrelease.h>
/* Simply sanity version stamp for modules. */
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_SMP "SMP "
#else
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_SMP ""
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_PREEMPT "preempt "
#else
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_PREEMPT ""
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULE_UNLOAD
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_MODULE_UNLOAD "mod_unload "
#else
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_MODULE_UNLOAD ""
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MODVERSIONS
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_MODVERSIONS "modversions "
#else
#define MODULE_VERMAGIC_MODVERSIONS ""
#endif
#ifndef MODULE_ARCH_VERMAGIC
#define MODULE_ARCH_VERMAGIC ""
#endif
#define VERMAGIC_STRING \
UTS_RELEASE " " \
MODULE_VERMAGIC_SMP MODULE_VERMAGIC_PREEMPT \
MODULE_VERMAGIC_MODULE_UNLOAD MODULE_VERMAGIC_MODVERSIONS \
MODULE_ARCH_VERMAGIC
VERMAGIC_STRING不仅包含内核版本号,还包含有内核使用的SMP与preempt, MODULE_UNLOAD, 架构等配置信息。模块在编译时,我们可以看到屏幕上会显示”MODPOST”。
<~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs> make
make -C ~/kernel/ SUBDIRS=~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs modules
make[1]: Entering directory '~/kernel'
CC [M] ~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs/my_debugfs.o
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
CC ~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs/my_debugfs.mod.o
LD [M] ~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs/my_debugfs.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory '~/kernel'
在此阶段, VERMAGIC_STRING会添加到模块的modinfo段。在内核源码目录下scripts\mod\modpost.c文件中可以看到模块后续处理部分的代码。模块编译生成后,通过modinfo my_debugfs.ko命令可以查看此模块的vermagic等信息。
<~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs> modinfo my_debugfs.ko
filename: ~/Documents/Demo/driver/debugfs/my_debugfs.ko
license: GPL
depends:
vermagic: 4.9.123 SMP preempt mod_unload aarch64
4.x 内核下的模块装载器里保存有内核的版本信息,在装载模块时,装载器会比较所保存的内核vermagic与此模块的modinfo段里保存的vermagic信息是否一致,两者一致时,模块才能被装载。
为了使两个版本一致:可以把 依赖源码中的include/linux/vermagic.h中的UTS_RELEASE修改成与目标机器的版本一致,这样,再次编译模块就可以了。
内核模块版本和内核版本不一致的处理方法
2, 发现版本号会追加git的版本号,还有个“+”
向linux内核版本号添加字符/为何有时会自动添加“+”号,根据这篇文章,一步一步试一下
第一步:去掉git的附加信息
先在menuconfig中找到
│ Symbol: LOCALVERSION [=] │
│ Type : string │
│ Prompt: Local version - append to kernel release │
│ Location: │
│ (1) -> General setup │
│ Defined at init/Kconfig:81 │
│ │
│ │
│ Symbol: LOCALVERSION_AUTO [=n] │
│ Type : boolean │
│ Prompt: Automatically append version information to the version string │
│ Location: │
│ (2) -> General setup │
│ Defined at init/Kconfig:91 │
│ Depends on: !COMPILE_TEST [=n] │
│
关掉LOCALVERSION_AUTO并留空LOCALVERSION,发现git版本确实是不见了,但是‘+’还是存在。
在scripts/setlocalversion文件中,找到以下语句:
# CONFIG_LOCALVERSION and LOCALVERSION (if set)
res="${res}${CONFIG_LOCALVERSION}${LOCALVERSION}"
# scm version string if not at a tagged commit
if test "$CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO" = "y"; then
# full scm version string
res="$res$(scm_version)"
else
# append a plus sign if the repository is not in a clean
# annotated or signed tagged state (as git describe only
# looks at signed or annotated tags - git tag -a/-s) and
# LOCALVERSION= is not specified
if test "${LOCALVERSION+set}" != "set"; then
scm=$(scm_version --short)
# res="$res${scm:++}" //××××××××××××××注释掉这句话××××××××××××
fi
fi
下面是注释前后的对比


问题解决。
MODVERSIONS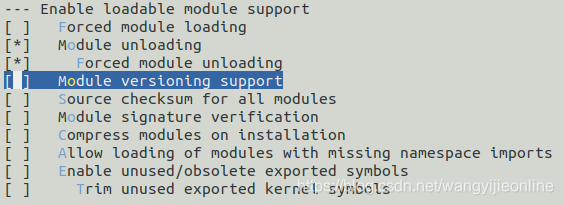
注意不要选图中那行
这个大家可以自行尝试一下
Prerequisites: The board should be running Linux and connected to terminal console.
Note: For log level debug support, the restool version should be LSDK-2003-RC1 or above and MC version should be 10.20.0 or above.
To check restool version:
$ root@localhost:~# restool -v
restool LSDK-20.04To check MC version:
root@localhost:~# restool -m
MC firmware version: 10.24.0For debugging, use the ls-debug script available in the LSDK rootfs. There is no need to create the debug object.
ls-debug -h | -h, –help | ls-debug help information |
| -ts, –timestamp=X | Enable/Disable timestamp printing, X is ON or OFF |
| -c, –console=X | Enable/Disable printing in UART console, X is ON or OFF |
| -l, –log=X | Enable/Disable printing in DDR log, X is ON or OF |
| -u, –uart=X | Set UART ID of the console, X = [0 – 4], 0 = OFF |
| -ll, –level=X | Set logging level, X = [0 – 5]0: Global1: Debug2: Info3: Warning4: Error5: Critical |
| -m, mem, –memory | Dump information about memory modules available |
| dpxy.z | Dump information about MC respective object |
For example, to enable logging in console with log level INFO:
$ ls-debug --log=on --console=on --level=2
dpdbg.0 created
DDR log printing ON
UART console printing ON
Log level set to 2
$ root@localhost:~# ls-debug --memory
Memory dumped information available in MC log/console
$ root@localhost:~# cat `find /dev/ -name "*mc_console"`
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_get_obj for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dpdbg_open on DPDBG
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dpdbg_dump on DPDBG
[I, DPNI] Memory info:
[I, DPNI] MC DDR #1 cacheable memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 134217728 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 14802708 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 119415020 bytes
[I, DPNI] MC DDR #1 non-cacheable memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 50331648 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 27680 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 50303968 bytes
[I, DPNI] DMEM1 memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 81920 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 27168 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 54752 bytes
[I, DPNI] DMEM2 memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 81920 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 27168 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 54752 bytes
[I, DPNI] DDR #1 memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 1610612736 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 143163392 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 1467449344 bytes
[I, DPNI] PEB memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 2097152 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 524288 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 1572864 bytes
[I, DPNI] DP-DDR memory
[I, DPNI] Total: 4294967296 bytes
[I, DPNI] Used: 0 bytes
[I, DPNI] Free: 4294967296 bytes
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dpdbg_close on DPDBG
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_close for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_set_irq_mask for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
[I, RESMAN] Handling command: dprc_set_irq_enable for DPRC 1 on portal id 0
root@localhost:~#1、通过读取系统文件节点获取相应CPU温度
cpu0:
cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp
cpu1:
cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone1/temp2、读取cpu温度失败问题
RK3288使用TSADC(Temperature-Sensor ADC)来测量CPU温度,支持两种模式:
用户自定义模式: 主动控制读取温度.
自动模式: 自动检测温度,达到阀值就自动报告.
dts配置如下:
&tsadc {
rockchip,hw-tshut-mode = <0>; /* tshut mode 0:CRU 1:GPIO */
rockchip,hw-tshut-polarity = <0>; /* tshut polarity 0:LOW 1:HIGH */
status = "okay";
};
tsadc: tsadc@ff280000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3288-tsadc";
reg = <0x0 0xff280000 0x0 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 37 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru SCLK_TSADC>, <&cru PCLK_TSADC>;
clock-names = "tsadc", "apb_pclk";
assigned-clocks = <&cru SCLK_TSADC>;
assigned-clock-rates = <5000>;
resets = <&cru SRST_TSADC>;
reset-names = "tsadc-apb";
pinctrl-names = "init", "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&otp_gpio>;
pinctrl-1 = <&otp_out>;
pinctrl-2 = <&otp_gpio>;
#thermal-sensor-cells = <1>;
rockchip,hw-tshut-temp = <95000>;
status = "disabled";
};用指令读取CPU温度:cat sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp,会报错/system/bin/sh: cat: temp: Invalid argumen。
看开机log,发现有如下报错:
clk: couldn’t get clock 0 for /tsadc@ff280000
说明tsadc缺少clock,查看dts,确实是少了这块。
xin32k: xin32k {
compatible = "fixed-clock";
clock-frequency = <32768>;
clock-output-names = "xin32k";
#clock-cells = <0>;
};以为这个时钟加上就好了,令人抓狂的是,就加了这么几行代码,机器竟然一直重启开不起机了。
加的这个地方是跟温度是相关的,那就从这个方面入手去思考找问题。会不会是检测到温度的过温阀值,导致重启的呢?
看硬件的连接上:
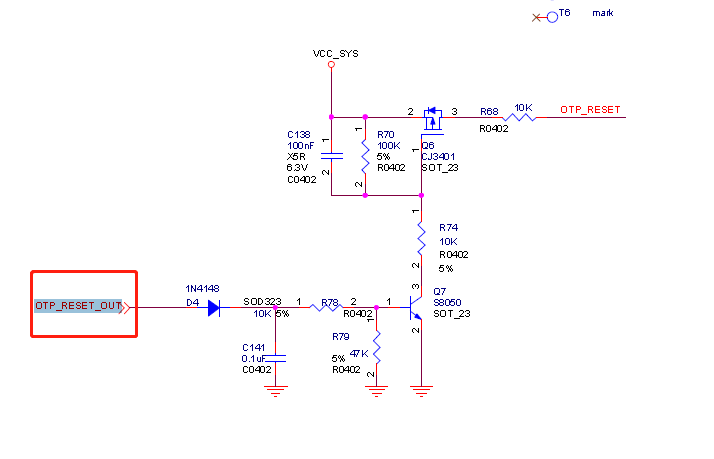
主控的OTP 引脚是有连接出来到pmic rk808的,如果这个阀值到了reset脚就会动作,然后重启。
由于没有硬性需求一定要这个温度到了阀值就重启的需求,这个时候可以把硬件上的连接电阻去掉,或者软件上把reset的io屏蔽掉。实际起作用的是:pinctrl-1 = <&otp_out>;
屏蔽掉,这时候机器就可以正常开机了。
再查看温度值:cat sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp
54111
就能正常读到温度值了。
不过不太能理解的是,配置里 rockchip,hw-tshut-temp = <95000>;是超过95度才重启,一开机应该也不会超过阀值才对,开机后读取的温度也就50°C。
romboot打印初步解析
本解析说明适用于: gxb/gxl/txl/axg/txhd/gxlx/gxlx2/txlx/g12A/G12B/SM1/TM2/A1/C1/C2/SC2/T5/T5D/T7/S4
romboot中默认将其打印从AO uart这一路输出
以gxb nand 平台为例,其romboot的打印如下:
GXBB:BL1:08dafd:0a8993;FEAT:E0FC3184;POC:3;RCY:0;EMMC:800;NAND:85;SD:0;READ:0;CHK:0;
其可以拆分为如下部分:
1. GXBB:主芯片内部代号
2. BL1:08dafd:0a8993;FEAT:E0FC3184; bootrom相关启动信息,安全相关的同事会用到。
3. POC:3; Power on Config信息。表明设备启动顺序,可以参考下面的表格:
POC 1st Boot device 2nd Boot device 3rd Boot device 4th Boot device
0 USB SPI NAND/eMMC SD Card
1 SPI NAND/eMMC SD Card USB
2 USB NAND/eMMC SD Card -
3 NAND/eMMC SD Card USB -
4. RCY:0; HDMI recovery接口读到的值,可以实现更改第一启动介质的目的,通常用于拯救烧错主存储介质的板子,在开发阶段尤为有用;
0为无hdmi recovery小板;
1为usb boot的hdmi recovery小板;
2为sdcard boot的hdmi recovery小板;
5. EMMC:800;NAND:85;SD:0;READ:0;CHK:0
这个是默认的主存储介质的启动顺序,依序为EMMC->NAND->SD->USB,这里因为有烧好的启动卡插入,所以直接在sdcard这里跳了出来;
EMMC:800, 为emmc初始化过程,800表示报错,数值具体对应到emmc控制器的SD_EMMC_STATUS寄存器,此处800表示为resoponse timeout,这个报错信息无法看出是init过程中哪一条命令报错,最为有效的debug方式为接PA进行分析;
如果平台有焊接emmc,在初始化过程报了非0值,可以参照如下表格来确认是那条线的焊接不良;
Field
Name
Description
7:0
Rxd_err
RX data CRC error per wire,
for multiple block read, the CRC errors are Ored together.
8
Txd_err
TX data CRC error,
For multiple block write, any one of blocks CRC error.
9
Desc_err
SD/eMMC controller doesn’t own descriptor.
The owner bit is “0”, set cfg_ignore_owner to ignore this error.
10
Resp_err
Response CRC error
11
Resp_timeout
No response received before time limit.
The timeout limit is set by cfg_resp_timeout.
12
Desc_timeout
Descriptor execution time over time limit.
The timeout limit is set by descriptor itself.
Consider the multiple block read/write, set the proper timeout limits.
在焊接了emmc的情况下,EMMC初始化打印不为0,通常是hw相关的问题,需要顺序检查以下几个项目:
1. vcc/vccq的供电及上电顺序,二者上电间隔太长可能会引起emmc的初始化失败,详情可以咨询hw的fengjie(jie.feng@amlogic.com)
2. 如果是EMMC初始化报Resp_timeout/Resp_err,需请hw同事检查emmc的cmd线的连通性
3. 如果是EMMC初始化报Rxd_err/txd_err,需请hw同事检查对应的报错data线的连通性
**
Add @ 20180209
在G12A上,SD card的romboot初始化会首先检查GPIOC6的电平状态,如果为card未插入,则romboot会打印SD:20000
**
NAND:85,为nand初始化过程报错,数值为错误码,常用错误码有
#define ERROR_NAND_TIMEOUT 0x81
#define ERROR_NAND_ECC 0x82
#define ERROR_NAND_MAGIC_WORD 0x83
#define ERROR_NAND_INIT_READ 0x84
#define ERROR_NAND_BLANK_PAGE 0x85
SD:0;READ:0;CHK:0,为SD卡初始化OK,读取OK,并且校验OK;对于其他存储介质,在初始化OK后,同样会进行READ和CHK动作,返回值为0,则为OK,非0值,则有其各自对应的错误码,这里不做详细描述1、修改设备树
vim components/firmware/uboot/arch/arm/dts/fsl-lx2160a-rdb.dts
&dpmac11 {
status = "okay";
phy-handle = <&sgmii_phy1>;
phy-connection-type = "sgmii";
};
sgmii_phy1: ethernet-phy@3 {
// RTL8211F PHY
compatible = "ethernet-phy-id001c.c916", "ethernet-phy-id004d.d072";
reg = <0x3>;
};
2、修改驱动
vim components/firmware/uboot/board/freescale/lx2160a/eth_lx2160ardb.c
/*Begin:add by zhaobaoxing for sgmii*/
srds_s2 = in_le32(&gur->rcwsr[28]) &
FSL_CHASSIS3_RCWSR28_SRDS2_PRTCL_MASK;
srds_s2 >>= FSL_CHASSIS3_RCWSR28_SRDS2_PRTCL_SHIFT;
/*End:add by zhaobaoxing for sgmii*/
/*Begin:add by zhaobaoxing for sgmii*/
if (get_board_rev() == 'C') {
setup_eth_rev_c(srds_s2);
goto next;
}
/*End:add by zhaobaoxing for sgmii*/
/*Begin:add by zhaobaoxing for sgmii*/
switch (srds_s2){
case 10:
wriop_set_phy_address(WRIOP1_DPMAC11, 0,
SGMII_PHY_ADDR1);
printf("warning: zhaobaoxing for serdes2\r\n");
break;
default:
printf("SerDes2 protocol 0x%x is not supported on LX2160ARDB\n",
srds_s2);
//goto next;
break;
}
/*End:add by zhaobaoxing for sgmii*/
3、修改功能宏定义
vim components/firmware/uboot/configs/lx2160ardb_tfa_defconfig
#CONFIG_DM_ETH=y1、修改设备树
&dpmac11 {
phy-handle = <&sgmii_phy1>;
phy-connection-type = "sgmii";
};
sgmii_phy1: ethernet-phy@3 {
// RTL8211F PHY
compatible = "ethernet-phy-id001c.c916", "ethernet-phy-id004d.d072";
reg = <0x3>;
};1、修改rcw文件
vim components/firmware/rcw/lx2160ardb_rev2/XGGFF_PP_HHHH_RR_19_5_2/rcw_2200_750_3200_19_5_2.rcw
SRDS_PRTCL_S1=3 #10G 8 #25G 17 CPRI-10G=3
SRDS_PRTCL_S2=10 #10 #CPRI 5 #-5GC #3#-BBU #5
SRDS_PRTCL_S3=3 #2
2、修改DPC文件
vim components/firmware/mc_utils/config/lx2160a/LX2160A-RDB/dpc-usxgmii.dts
ports {
mac@3 {
/*Begin:changed by zhaobaoxing for 10G sfp+*/
/*link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_PHY";
enet_if = "USXGMII";
*/
/*End:changed by zhaobaoxing for 10G sfp+*/
link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_FIXED";
enet_if = "XFI";
};
mac@4 {
/*Begin:changed by zhaobaoxing for 10G sfp+*/
/*link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_PHY";
enet_if = "USXGMII";
*/
/*End:changed by zhaobaoxing for 10G sfp+*/
link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_FIXED";
enet_if = "XFI";
};
mac@11 {
link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_PHY";
};
mac@17 {
link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_PHY";
};
mac@18 {
link_type = "MAC_LINK_TYPE_PHY";
};
};
3、修改dpl文件
vim components/firmware/mc_utils/config/lx2160a/LX2160A-RDB/dpl-eth.19.dts
connections {
connection@1{
endpoint1 = "dpni@0";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@3";
};
connection@2{
endpoint1 = "dpni@1";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@4";
};
connection@3{
endpoint1 = "dpni@2";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@5";
};
connection@4{
endpoint1 = "dpni@3";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@6";
};
connection@5{
endpoint1 = "dpni@4";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@7";
};
connection@6{
endpoint1 = "dpni@5";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@8";
};
connection@7{
endpoint1 = "dpni@6";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@9";
};
connection@8{
endpoint1 = "dpni@7";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@10";
};
connection@9{
endpoint1 = "dpni@8";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@11";
};
connection@10{
endpoint1 = "dpni@9";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@12";
};
connection@11{
endpoint1 = "dpni@10";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@17";
};
connection@12{
endpoint1 = "dpni@11";
endpoint2 = "dpmac@18";
};
};