import os
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
master = tk.Tk()
entry1_str = tk.StringVar()
def helloCallBack():
entry1_str.set("好的回购好的回购好的回购好的回购好的回购好的回购")
print("hello word")
def gui():
master.title("Lable家族")
master.geometry("800x480")
master.update()
theLableFrame = tk.LabelFrame(master,text="文件列表",padx=5, pady=5,bd=5)
theLableFrame.pack(fill=BOTH, expand=YES, padx=10, pady=10)
theLable = tk.Label(theLableFrame,width = master.winfo_width(),wraplength = 80,anchor=NW,textvariable=entry1_str)
theLable.pack(fill=BOTH, expand=YES, padx=10, pady=10)
theButton = tk.Button(master, text ="点我", command = helloCallBack)
theButton.pack(side='bottom')
master.mainloop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gui()
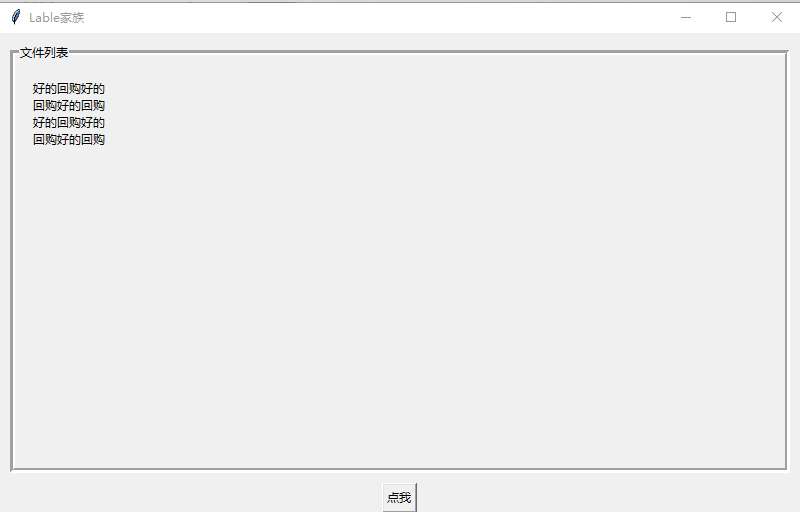
实现效果图如下: